Charge Carrier Recombination Dynamics of Semiconductor Photocatalysts
Photocatalysis, the induction of chemical changes by absorption of light, has applications ranging from water splitting for hydrogen production, removal of pollutants from water, and artificial photosynthesis. With this wide spread of applications, earth-abundant photocatalysts are attracting extensive interest, especially those based on anatase (TiO2) due to its abundance, low toxicity and low cost. However due to its wide bandgap at 3.2 eV, it is not a good absorber in the visible range. Viable routes to extend its absorption include doping with transition metals to induce defect states in the lattice and tune the bandgap towards the visible. In this application note, by means of time-resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy, we study the dynamics of charge carriers in copper nitrogen doped titanium oxide (Cu-NTiO2).
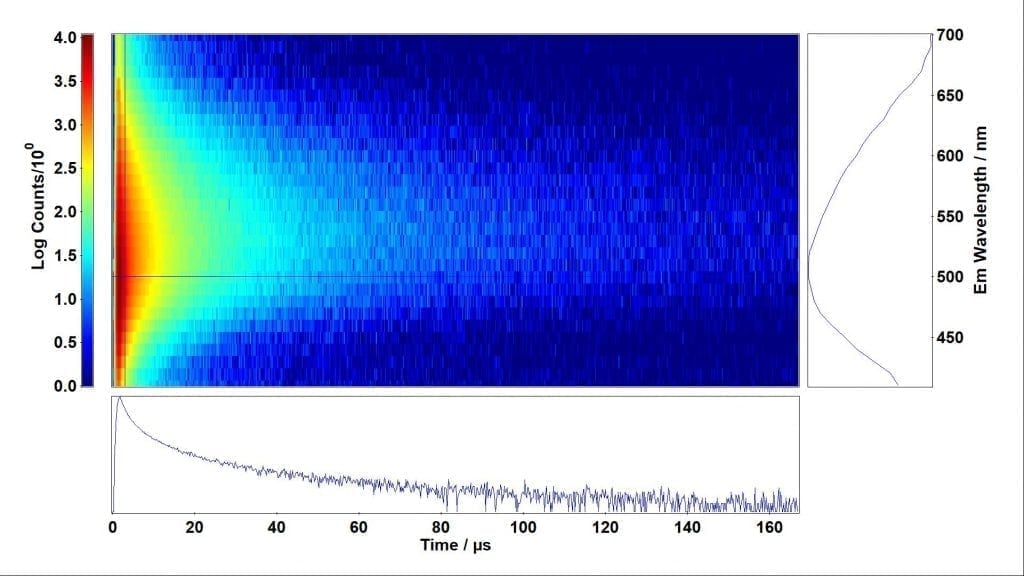
Figure 1: Time-resolved emission spectrum of a Cu-N-TiO2 photocatalyst
Download the Full Photocatalysts Application Note
Charge Carrier Recombination Dynamics of Semiconductor Photocatalysts
Sign-Up for our Application and Technical Notes
If you have enjoyed reading our Application Note, why note sign-up to our infrequent newsletter via our red Sign-up button below.