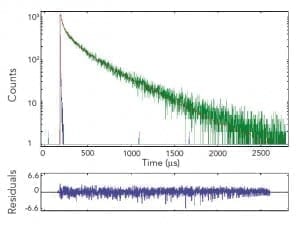
Phosphorescence Lifetime
Phosphorescence lifetimes, occurring as emissive decays from the triplet-state, can also be approximated as those decays occurring in the time region from tens of nanoseconds to seconds.
Phosphorescence lifetime measurements are carried out using a technique called Multi-Channel Scaling (MCS) and this is used for the acquisition of sample decays.
For further information or to discuss your requirements, please contact us.
Description
Photons are counted in a time window which sweeps across the full time range following each excitation pulse, creating a histogram of counts versus time. The data quality of the resulting histogram is improved by adding the data of repeated sweeps.
The sample is excited, and data are collected repetitively with a low to medium repetition rate source, such as the standard microsecond flashlamp (μF2), or lasers operating in the kHz regime.
Products
Applications
- Lifetime Measurements of Lanthanides
- Time-Resolved Singlet Oxygen Measurements
- Fluorescence Resonance Energy transfer (FRET)
Publications
| Author | Year | Title | Journal | Additional details | Volume | Pages | Instruments | Publication details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xixi Qin et al. | 2016 | Hybrid coordination-network-engineering for bridging cascaded channels to activate long persistent phosphorescence in the second biological window | Nature Scientific Reports Volume:6 Pages:20275 Year:2016 | Journal:Nature Scientific Reports Volume:6 Pages:20275 Year:2016 Instruments | 6 | 20275 | Hybrid coordination-network-engineering for bridging cascaded channels to activate long persistent phosphorescence in the second biological window Author:Xixi Qin et al.Further info | |
| Linlin Liu et al. | 2015 | Near-infrared quantum cutting in Nd^3+ and Yb^3+ Doped BaGd_2ZnO_5 phosphors | Optical Materials Express Volume:5 Pages:756-763 Year:2015 | Journal:Optical Materials Express Volume:5 Pages:756-763 Year:2015 Instruments | 5 | 756-763 | Near-infrared quantum cutting in Nd^3+ and Yb^3+ Doped BaGd_2ZnO_5 phosphors Author:Linlin Liu et al.Further info Journal:Optical Materials Express Volume:5 Pages:756-763 Year:2015 Instruments | |
| Karolina Fiaczyk et al. | 2015 | Photoluminescent Properties of Monoclinic HfO2:Ti Sintered Ceramics in 16–300 K | J. Phys. Chem. Volume:119(9) Pages:5026-5032 Year:2015 | Journal:J. Phys. Chem. Volume:119(9) Pages:5026-5032 Year:2015 Instruments | 119(9) | 5026-5032 | Photoluminescent Properties of Monoclinic HfO2:Ti Sintered Ceramics in 16–300 K Author:Karolina Fiaczyk et al.Further info | |
| V. Cherpak, et. al | 2014 | Efficient “Warm-White” OLEDs Based on the Phosphorescent bis-Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complex | Journal of Physical Chemistry C Volume:118(21) Pages:11271-11278 Year:2014 | Journal:Journal of Physical Chemistry C Volume:118(21) Pages:11271-11278 Year:2014 Instruments | 118(21) | 11271-11278 | Efficient “Warm-White” OLEDs Based on the Phosphorescent bis-Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complex Author:V. Cherpak, et. alFurther info Journal:Journal of Physical Chemistry C Volume:118(21) Pages:11271-11278 Year:2014 Instruments |